Have you ever wondered what happens inside your camera the moment you press the shutter button? How does it capture the world around you and turn it into a clear, vibrant photo?
Understanding how a camera works can give you a new appreciation for this incredible device you use every day. You’ll discover the simple steps your camera takes to freeze moments in time, whether it’s a digital camera, a smartphone, or a classic film camera.
Keep reading, and soon you’ll see your camera in a whole new light—literally!
Camera Basics
Cameras capture moments by controlling light and focus. Understanding camera basics helps you see how images form. Each part plays a key role in making photos clear and bright.
Light enters the camera and passes through different parts. These parts work together to record what you see. Let’s explore how lenses, sensors, shutters, and apertures work.
Lens And Light
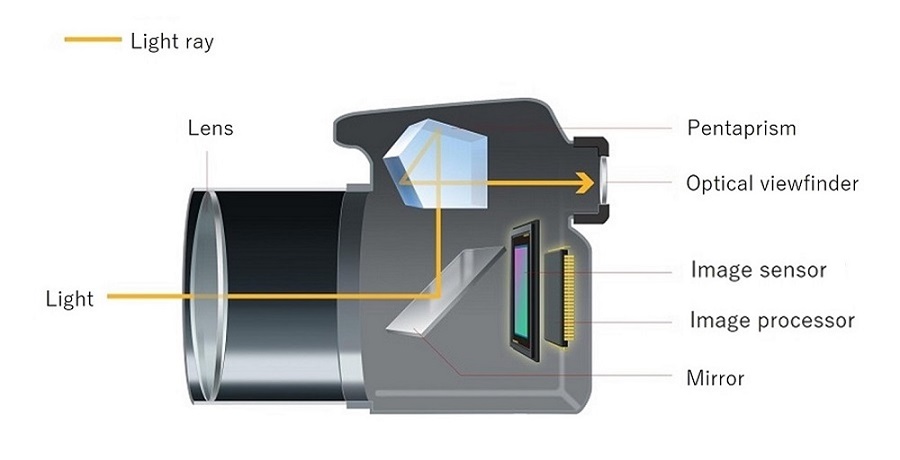
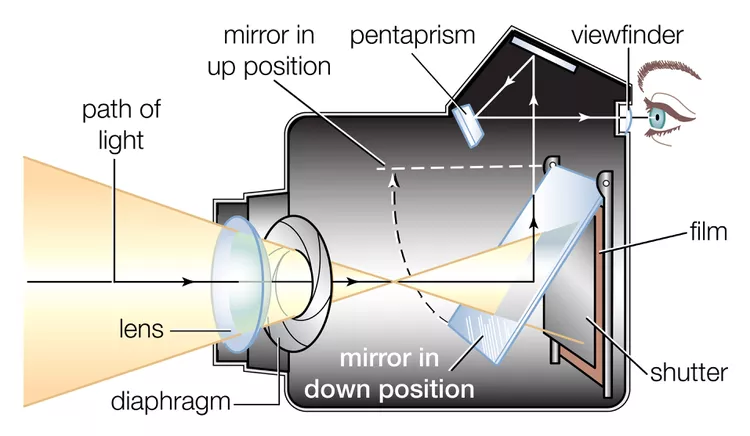
The lens directs light into the camera. It focuses light rays to create a sharp image. Different lenses change how much you see and how close the image looks. The lens controls light paths to capture clear photos.
Image Sensors
Image sensors change light into digital signals. They are inside the camera behind the lens. Sensors have tiny cells that detect light intensity and color. This data forms the digital image you see on screens.
Shutter And Aperture
The shutter controls how long light hits the sensor. It opens and closes quickly to freeze motion or blur it. The aperture adjusts the size of the opening that lets light in. It affects brightness and depth of field in photos.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Digital Camera Components
Digital cameras have several key parts that work together to capture and save photos. Each component plays a specific role in turning light into a clear, colorful image. Understanding these parts helps explain how digital cameras create the pictures we see.
Image Processing
The image sensor captures light and converts it into electrical signals. These signals are raw data and need to be processed. The camera’s processor adjusts colors, brightness, and sharpness to create a final image. This step also reduces noise and improves detail. Fast processing helps the camera take many photos quickly.
Memory Storage
After processing, the image data is saved on memory cards. Common types include SD cards and microSD cards. These cards store thousands of photos and videos. The camera writes data quickly so you do not miss any moments. Storage size varies, letting users choose based on their needs.
Display Screens
Most digital cameras have a screen to show photos immediately. This screen helps users check if the picture is good. Some cameras have touchscreen displays for easy control. The screen also shows menus and settings, making the camera easier to use. Bright, clear screens work well even in sunlight.
Credit: everpresent.com
How Cameras Capture Images
Cameras capture images by transforming light into digital information. This process starts the moment light enters the camera lens. The camera then converts this light into signals that form the picture you see. Understanding this conversion helps reveal how cameras work behind the scenes.
Light To Digital Signal
Light passes through the camera lens and hits the image sensor. The sensor is made of millions of tiny cells called pixels. Each pixel measures the brightness of the light that hits it. The sensor changes this light into electrical signals. These signals are the camera’s way of recording the image.
Image Formation
The camera’s processor collects the electrical signals from the sensor. It arranges these signals to create a full image. The processor adjusts the signals to match the scene’s details and sharpness. This step shapes the final picture you see on the screen.
Color And Resolution
Cameras use filters to capture color information. Each pixel records red, green, or blue light. The camera combines these colors to recreate the original scene. Resolution depends on the number of pixels. More pixels mean more detail and clearer images.
Types Of Cameras
Cameras come in many types. Each type works a little differently. Knowing about these helps you choose the right one. The main types include DSLR, mirrorless, and smartphone cameras. Each has unique features and uses.
Dslr Cameras
DSLR stands for Digital Single-Lens Reflex. These cameras use a mirror inside to show the image through the lens. When you take a photo, the mirror flips up. This lets light reach the image sensor. DSLRs are known for high image quality and fast focus. They have many lens options. They are popular with serious photographers.
Mirrorless Cameras
Mirrorless cameras do not have a mirror inside. Light goes straight to the image sensor. This makes the camera smaller and lighter. They use electronic viewfinders instead of optical ones. Mirrorless cameras offer fast shooting and good video quality. They are easy to carry and becoming very popular.
Smartphone Cameras
Smartphone cameras are built into mobile phones. They use small lenses and sensors. These cameras are very convenient. They include software to improve photos automatically. Smartphone cameras are good for everyday use. They allow quick sharing of pictures online.
Factors Affecting Photo Quality
Photo quality depends on several key factors inside the camera and the environment. Each factor influences how sharp, bright, and clear the image will be. Understanding these helps you take better pictures and improve your photography skills.
Focus And Depth Of Field
Focus controls which part of the image appears sharp. Cameras adjust focus by moving the lens elements. Depth of field means how much of the image is in focus from front to back. A shallow depth of field blurs the background, making the subject stand out. A deep depth of field keeps most of the scene sharp. Adjusting focus and depth of field shapes the photo’s look and feel.
Exposure Settings
Exposure settings control how much light hits the camera sensor. The three main settings are aperture, shutter speed, and ISO. Aperture size affects brightness and depth of field. Shutter speed controls how long light enters the camera. ISO changes the sensor’s sensitivity to light. Proper exposure balances these settings to avoid too dark or too bright photos.
Lighting Conditions
Lighting greatly affects photo quality. Natural light often gives soft, even illumination. Artificial light can add color or harsh shadows. The direction and strength of light change how details and colors appear. Low light can cause noise or blur. Bright light can cause glare or lose detail. Managing light helps produce clear and vibrant images.
Secrets Behind Stunning Photos
Stunning photos capture attention and tell stories without words. They show more than just a scene; they reveal emotion, depth, and beauty. Understanding the secrets behind these photos helps anyone create images that stand out.
Great photography blends simple techniques with creativity. It uses tools like light, shadow, and composition to shape what the viewer sees. Even basic cameras can produce amazing results with the right approach.
Composition Techniques
Composition is the arrangement of elements in a photo. It guides the viewer’s eye and creates balance. Techniques like the rule of thirds place the subject off-center to add interest. Leading lines draw attention and create depth. Framing uses natural borders to focus on the subject. Simple backgrounds help keep the focus clear and strong.
Use Of Light And Shadow
Light shapes every photo. Soft light reduces harsh shadows and brings out details. Golden hour, just after sunrise or before sunset, offers warm, flattering light. Shadows add contrast and texture, making images more dynamic. Directional light highlights shapes and forms. Controlling light helps create mood and drama in photos.
Post-processing Tips
Post-processing improves photos by adjusting colors, brightness, and sharpness. Cropping can fix composition and remove distractions. Increasing contrast makes images pop. Removing noise cleans up low-light shots. Subtle edits keep photos natural while enhancing their best features. Using simple tools can make a big difference.
Privacy And Security
Privacy and security are important when using cameras. Cameras can capture images and videos without our knowledge. This raises concerns about spying and data theft. Knowing how to protect yourself helps keep your privacy safe.
Understanding how to detect cameras and control permissions reduces risks. It also helps prevent unauthorized recording and sharing of your personal moments.
Detecting Active Cameras
Active cameras often show small indicator lights. Look for green or orange dots on phones and webcams. Some cameras blink when recording. Watch for unusual device behavior like fast battery drain. These signs may reveal hidden or active cameras nearby.
Checking Device Permissions
Check your device settings for camera access. Review which apps have permission to use the camera. Disable access for apps you do not trust. Regularly updating permissions limits unwanted spying. This simple step improves your digital privacy significantly.
Finding Hidden Cameras
Hidden cameras can be hard to spot. Use a flashlight to scan for lens reflections. Small glass lenses will reflect light differently. Specialized RF detectors can find wireless camera signals. Inspect suspicious objects carefully in private spaces.
Credit: everpresent.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Cameras Capture What We See?
Cameras capture images by letting light pass through a lens onto a sensor. The sensor converts light into electrical signals. The camera processes these signals into digital images stored on memory cards. This process mimics how our eyes see and record what is in front of us.
How Do I Know If A Camera Is Watching?
Check for indicator lights on devices, unusual battery or data use, unknown apps, and use a flashlight to spot hidden lenses. Review privacy settings for camera access and scan your Wi-Fi for unknown devices.
How Does A Camera Catch An Image?
A camera catches an image by letting light enter through the lens onto a sensor or film. The sensor records light patterns. The camera processes this data to create a visible photo stored digitally or on film.
Are Cameras Always Recording?
Cameras do not always record. Recording depends on settings, motion detection, or manual activation. Many operate only when triggered.
Conclusion
A camera captures light through its lens to create images. The light hits a sensor, which records the scene. Then, the camera processes this information into a photo. Different cameras use various technologies but follow this basic idea. Understanding how cameras work helps you take better pictures.
It also makes photography less confusing and more fun. Keep exploring your camera’s features to improve your skills. Now, you know the simple steps behind every shot you take.
