Have you ever wondered how some devices work so fast? Like smart speakers or self-driving cars? They make quick decisions without waiting a long time. This speed is often because of something called edge computing. In this article, we will explain edge computing in simple words. You will learn what it is, why it matters, and where it is used.
What Is Edge Computing?
Edge computing means processing data near where it is made. Think of it like this: instead of sending all information far away to a big computer, edge computing uses small computers close by. These small computers can be inside a device or near it. This way, data does not have to travel far. It saves time and makes things faster.
Imagine you have a smart camera at home. It records video all day. Without edge computing, the camera would send all video to a far cloud computer to check it. This can take time and use a lot of internet. With edge computing, the camera can check the video itself first. It can decide quickly if something important happens. Then, it only sends the important parts to the cloud.

Credit: www.youtube.com
How Edge Computing Works
Here is a simple way to see the difference between edge computing and traditional cloud computing:
| Traditional Cloud Computing | Edge Computing |
|---|---|
| Your device sends all data far away to a big cloud server. | Your device or a nearby small server processes data first. |
| The cloud processes everything and sends back answers. | The local device makes fast decisions and sends only summaries to cloud. |
| It can be slow if the internet connection is weak. | It works even if the internet is slow or lost. |
Why Is Edge Computing Useful?
Edge computing is useful for many reasons. Here are the main benefits:
- Speed: It gives faster answers because data is processed close to where it is made. This is called low latency.
- Less Internet Use: It reduces the amount of data sent on the internet. This saves bandwidth and lowers costs.
- Works Offline: Edge computing can work even if the internet connection is weak or lost. This makes it more reliable.
- Privacy: Since data is processed locally, sensitive information does not have to travel far. This can protect privacy.
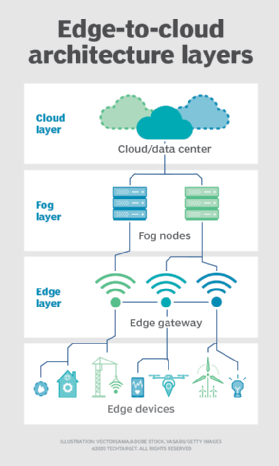
Credit: www.techtarget.com
Examples of Edge Computing
Edge computing is used in many devices and places. Here are some easy examples:
- Smart Speakers: Devices like smart speakers understand your voice commands locally before sending data to the cloud.
- Factory Robots: Robots in factories check sensor data on-site to stop problems quickly.
- Self-Driving Cars: Cars use edge computing to make fast driving decisions without delay.
- Health Devices: Wearable health devices can process data locally to alert users immediately.
- Smart Cameras: Cameras can analyze video on the device and send alerts when needed.
Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing
It is important to know how edge computing differs from cloud computing:
| Cloud Computing | Edge Computing |
|---|---|
| Data is sent to big, far-away data centers. | Data is processed close to the device or user. |
| Good for heavy data storage and big tasks. | Good for fast tasks and real-time decisions. |
| Needs a strong internet connection all the time. | Can work even with slow or no internet. |
| Can take more time to send and receive data. | Works quickly because data does not travel far. |
Why Do We Need Edge Computing Now?
The world has many new smart devices. These devices create a lot of data. Sending all this data to the cloud is slow and uses a lot of internet. Some devices need to act quickly. For example, a self-driving car must make fast decisions to stay safe. Edge computing helps devices work faster and better.
Also, some places do not have good internet. Edge computing lets devices work well even there. This helps in factories, farms, and faraway locations.
What Are the Challenges of Edge Computing?
While edge computing is helpful, it has some challenges:
- Cost: Setting up many small computers near devices can be expensive.
- Security: More devices mean more places to protect from hackers.
- Management: Managing many small computers can be harder than managing one big cloud.
- Power: Some edge devices need good power sources to work well.
Despite these challenges, many companies use edge computing to improve speed and reliability.
How Does Edge Computing Help Everyday Life?
Edge computing makes many daily activities better. Here are some ways:
- Faster Voice Commands: Your smart speaker answers you quickly.
- Better Internet Games: Games run smoothly with less delay.
- Quick Emergency Alerts: Health devices warn you right away.
- Safer Driving: Cars react fast to road dangers.
- Smart Homes: Devices control lights and temperature instantly.
Simple Summary
Edge computing means using small computers near where data is made. This helps devices work faster and safer. It reduces internet use and works well even if the internet is slow. Many smart devices, cars, and factories use edge computing today. Though it has some challenges, edge computing is growing fast. It makes our technology smarter and more reliable.
Final Thoughts
Now you know what edge computing is. It is a way to bring computing close to devices. This helps with speed, reliability, and privacy. Edge computing is important for many new technologies. It helps devices make quick decisions without delay. As more smart devices appear, edge computing will become more common.
If you use smart devices, you are already using edge computing. It is part of how modern technology works. Understanding edge computing helps you see how the future of technology may grow.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Edge Computing In Simple Terms?
Edge computing processes data near its source, like devices or local servers, instead of distant cloud centers. This reduces delay, saves bandwidth, and boosts real-time decision-making. It supports faster responses for applications like autonomous cars and smart sensors by handling information instantly at the network’s edge.
How Does Edge Computing Work Step By Step?
Edge computing processes data near its source, like devices or local servers. Devices collect data, analyze it instantly, and act fast. Only essential data sends to the cloud for storage or further analysis. This reduces latency, saves bandwidth, and improves real-time responsiveness in applications.
Is Edge Faster Than 5g?
Edge computing processes data locally, reducing latency and speeding response times. It is faster than 5G for real-time actions. 5G offers high-speed wireless connectivity, but edge computing delivers quicker results by handling data near the source, enhancing speed for critical applications.
What Are The Three Basic Components Of Edge Computing?
The three basic components of edge computing are edge devices, edge servers, and network connectivity. Edge devices collect data locally. Edge servers process data near the source. Network connectivity links devices to servers and the cloud. These components enable fast, efficient data processing at the network edge.
